Have you ever wondered what makes your car respond effortlessly to your slightest touch on the steering wheel? It’s all thanks to the ingenious invention known as power steering. From nimble city driving to effortless highway cruising, power steering plays a pivotal role in enhancing your driving experience.
Power steering is a mechanical or hydraulic system designed to aid the driver in turning the wheels with minimal effort. It utilizes various components to reduce the physical exertion required to steer, allowing for precise control and smoother handling.
This technological advancement has revolutionized the automotive industry, making driving more comfortable, convenient, and accessible to a wider range of individuals. In this article we’ll explore how power steering works, different types of power steering systems available on the market, and how to troubleshoot a faulty power steering system.

Understanding Power Steering
Power steering is an essential component of modern vehicles, enhancing the driving experience by making steering effortless and more responsive. To fully understand power steering and its significance, let’s delve into its workings and compare it to the traditional manual steering system.
Power steering is a mechanism that assists the driver in turning the vehicle’s wheels with minimal effort. Its primary purpose is to reduce the amount of force required to steer the vehicle, particularly at low speeds and during parking maneuvers. By providing additional assistance, power steering enhances maneuverability and control, making it easier for drivers to navigate their vehicles.
Manual Steering vs. Power Steering Systems
In manual steering systems, the driver relies solely on mechanical force to turn the wheels. This type of steering can be physically demanding, especially in larger or heavier vehicles. Mechanical steering racks work fine when the vehicle is moving at any kind of speed. However, once the vehicle is static, turning the wheels in place becomes a tug of war with the steering wheel. This is where power steering systems come into play. They utilize various mechanisms to amplify the driver’s steering input, resulting in smoother and more manageable steering.
Hydraulic and Electric Power Steering Systems
There are two primary types of power steering systems: hydraulic power steering (HPS) and electric power steering (EPS).
Hydraulic Power Steering System
Hydraulic power steering systems have been widely used in vehicles for several decades. These systems rely on hydraulic pressure generated by a power steering pump to assist the driver’s steering effort. The power steering pump is driven by the engine and pressurizes hydraulic fluid, which is then transmitted to the steering gear or rack and pinion assembly. The hydraulic pressure assists in turning the wheels, making steering easier for the driver.
Components of a Hydraulic Power Steering System
A hydraulic power steering system comprises several key components:
Power Steering Pump – The power steering pump is typically driven by the vehicle’s engine via a belt. Its primary function is to pressurize the power steering fluid, creating the necessary hydraulic force to assist with steering. The pump draws fluid from the reservoir and circulates it through the system.
Power Steering Fluid and Reservoir – Power steering fluid serves as the hydraulic medium within the system. It provides lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic pressure for smooth steering operation. The power steering fluid reservoir stores an adequate supply of fluid and allows for fluid expansion and contraction.
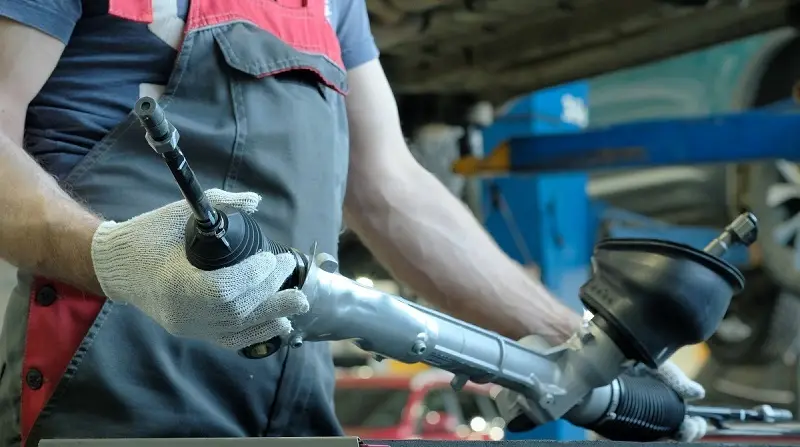
Steering Gear or Rack and Pinion – The steering gear, also known as the rack and pinion assembly, converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement, turning the vehicle’s wheels. It contains a gear mechanism and a rack that engages with the steering linkage, allowing for precise control over the direction of the wheels.
Power Steering Hoses and Hydraulic Lines – Power steering hoses and hydraulic lines transport pressurized fluid between the power steering pump, steering gear, and other relevant components. These hoses and lines are designed to withstand high-pressure conditions and ensure the proper flow of fluid throughout the system.
Functioning of a Hydraulic Power Steering System
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a series of events occur within a hydraulic power steering system:
- Steering Wheel Input – The driver applies force to the steering wheel, initiating a rotational movement.
- Power Steering Pump Activation – As the driver turns the steering wheel, a valve mechanism within the steering gear detects the movement and signals the power steering pump to activate.
- Fluid Pressure Generation – The power steering pump pressurizes the power steering fluid and sends it through the hoses or hydraulic lines to the steering gear.
- Steering Assistance – The pressurized fluid enters the steering gear, exerting force on the rack and pinion mechanism. This force assists in moving the wheels according to the driver’s steering input, reducing the effort required.
- Return of Fluid – After assisting with steering, the fluid returns to the power steering pump and gets recirculated through the system. The power steering pump continues to provide assistance as long as the steering wheel is being turned.
Electric Power Steering System
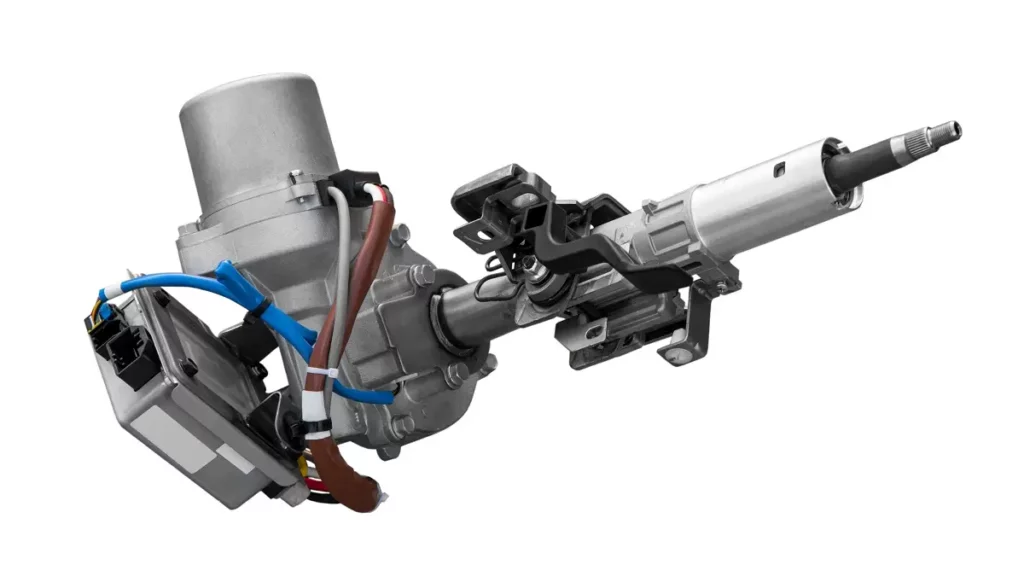
Electric power steering systems have gained popularity in recent years due to their efficiency and versatility. Instead of hydraulic pressure, these systems employ an electric motor to assist the driver’s steering inputs.
The electric power steering motor is connected to the steering column and can adjust the steering assistance based on various factors such as vehicle speed and driving conditions. Electric power steering systems are generally lighter, more fuel-efficient, and offer greater flexibility in terms of customization and integration with other vehicle systems.
Components of an Electric Power Steering System
An electric power steering system consists of several key components:
Electric Power Steering Motor – The electric power steering motor is the heart of the system. It is typically located on the steering column or the steering rack. The motor generates torque based on the driver’s steering input and provides the necessary assistance for turning the wheels.
Power Steering Controller – The power steering controller, often integrated into the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU), acts as the brain of the EPS system. It receives inputs from various sensors and the steering column torque sensor to determine the required level of assistance from the electric power steering motor.
Steering Column Torque Sensor – The steering column torque sensor detects the amount of torque or rotational force applied to the steering column by the driver. This information is sent to the power steering controller, which adjusts the assistance provided by the electric power steering motor accordingly.
Vehicle Speed Sensor – The vehicle speed sensor measures the speed of the vehicle. It provides input to the power steering controller to modulate the level of assistance based on the driving conditions. Higher assistance may be provided at lower speeds for easy maneuverability, while lower assistance may be given at higher speeds for better road feel.
Benefits of Electric Power Steering
Electric power steering systems offer several advantages over hydraulic power steering systems, including:
Improved Fuel Efficiency – Electric power steering systems are more energy-efficient compared to hydraulic systems since the electric motor only consumes power when assistance is required. This efficiency leads to improved fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Customization and Control – EPS systems provide greater flexibility in adjusting the steering feel and response. The power steering controller can be programmed to offer different levels of assistance, allowing for customization based on the vehicle’s characteristics or driver preferences.
Integration with Vehicle Systems – Electric power steering systems can be seamlessly integrated with other vehicle systems, such as driver-assistance features and stability control systems. This integration allows for improved coordination and enhanced overall vehicle performance.
Different Types of Electric Power Steering Systems:
There are various types of electric power steering systems:
Column-Assist Electric Power Steering – In this type of EPS system, the electric motor is mounted on the steering column, assisting the driver’s steering efforts directly.
Rack-Assist Electric Power Steering – In a rack-assist EPS system, the electric motor is integrated into the steering rack assembly. This design provides a more direct and precise steering response.
Pinion-Assist Electric Power Steering – Pinion-assist EPS systems feature the electric motor located on the steering gear pinion. This design offers a compact and lightweight solution.
Understanding the components and functioning of an electric power steering system provides insights into its advantages and various configurations. In the subsequent sections, we will explore common causes of electric power steering failures, symptoms of issues, and essential maintenance practices for optimal performance.
Power Steering Failure Causes

Power steering failures can occur in both hydraulic and electric power steering systems. Understanding the common causes of power steering failures is essential for diagnosing and addressing issues promptly. Let’s explore some of the primary reasons why power steering systems can fail.
Lack of Power Steering Fluid
In hydraulic power steering systems, a common cause of failure is a low or inadequate level of power steering fluid. Insufficient fluid can result from leaks, improper maintenance, or a worn-out power steering pump. When the fluid level is low, the system may not generate enough hydraulic pressure to provide the necessary assistance, leading to stiff or difficult steering.
Get quality power steering fluid for your BMW!
Worn-out or Damaged Power Steering Belts and Pulleys
In hydraulic power steering systems, power is transferred from the engine to the power steering pump via a belt. Over time, these belts can become worn, loose, or damaged, affecting the pump’s performance. Similarly, damaged or misaligned power steering pump pulleys can lead to belt slippage, reducing the power steering pump’s efficiency and causing steering issues.
Get quality replacement parts for your power steering system!
Issues with the Power Steering Pump or Motor
Both hydraulic and electric power steering systems can experience problems with their respective pumps or motors. In hydraulic systems, a failing power steering pump may struggle to generate adequate pressure, resulting in diminished steering assistance. Electric power steering motors can encounter electrical or mechanical faults, leading to a complete loss of steering assistance or intermittent operation.
Find a replacement power steering pump!
Leaking Power Steering Hoses and Seals
Power steering systems utilize hoses and seals to transport pressurized fluid. Over time, these components can develop leaks due to wear, aging, or damage. Leaking hoses or seals result in a loss of power steering fluid, which reduces the system’s hydraulic pressure and affects steering performance.
Get quality power steering lines!
Faulty Sensors or Control Modules
In electric power steering systems, issues can arise from faulty sensors or control modules. Malfunctioning sensors, such as the steering column torque sensor or vehicle speed sensor, may provide inaccurate information to the power steering controller, leading to improper steering assistance. Additionally, problems with the power steering controller itself can disrupt the system’s functionality.
Symptoms of Power Steering Failure
Recognizing the symptoms of power steering failure is vital for addressing issues promptly and preventing further damage to the system. Here are some common indicators that suggest problems with the power steering system:
Difficulty in Turning the Steering Wheel
One of the primary signs of power steering failure is an increased effort required to turn the steering wheel. You may experience stiffness or resistance when attempting to steer the vehicle, particularly at lower speeds or during parking maneuvers. This can make it challenging to maneuver the vehicle effectively.
Unusual Noises When Steering
Power steering problems can produce abnormal noises. If you hear a squealing, whining, or groaning sound when turning the steering wheel, it may indicate a worn-out or failing power steering pump or belt. Additionally, air trapped in the power steering system can cause a bubbling or gurgling noise.
Vibration or Jerking Sensations While Driving
A malfunctioning power steering system can cause vibrations or jerking sensations in the steering wheel while driving. These vibrations may be accompanied by an inconsistent or unpredictable steering feel, making it challenging to maintain a steady course.
Warning Lights Related to Power Steering
Some vehicles are equipped with warning lights specifically designed to indicate power steering issues. If you see a power steering warning light illuminated on your dashboard, it is essential to have the system inspected as soon as possible.
Gradual Loss of Power Steering Assistance
In certain cases, power steering failure may occur gradually rather than abruptly. You may notice a progressive decrease in the amount of steering assistance provided by the system. This loss of assistance can make steering increasingly difficult and should be addressed as soon as possible.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other underlying problems with the steering or suspension systems. If you experience any of these signs, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or service professional for a comprehensive diagnosis and appropriate repairs.
In the next section, we will discuss troubleshooting techniques and steps to identify and resolve power steering issues effectively.
Troubleshooting Power Steering Issues

When faced with power steering problems, it’s essential to follow a systematic troubleshooting approach to identify and resolve the underlying issues. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot power steering problems:
Step 1: Check Power Steering Fluid Levels – Begin by checking the power steering fluid reservoir. Ensure that the fluid level is within the recommended range. If the fluid level is low, it may indicate a leak or other issues within the system. Top up the fluid if necessary, but also be mindful of addressing any underlying leaks.
Step 2: Inspect Power Steering Belts, Pulleys, and Hoses – Examine the condition of the power steering belts, pulleys, and hoses. Look for signs of wear, damage, or looseness. Tighten or replace loose or worn-out belts, and repair or replace damaged hoses or pulleys as needed. Ensure proper alignment and tension of the belts.
Step 3: Assess Power Steering Pump or Motor Functionality – For hydraulic power steering systems, listen for unusual noises coming from the power steering pump when the engine is running. If the pump is excessively noisy or fails to provide adequate assistance, it may need to be repaired or replaced. In electric power steering systems, check for proper operation of the electric power steering motor and control modules.
Step 4: Look for Leaks – Inspect the power steering system for any visible leaks. Check the power steering hoses, seals, and connections for signs of fluid leakage. Address any leaks by repairing or replacing the affected components.
It’s important to remember that power steering systems can be complex, and attempting extensive repairs without the necessary knowledge and expertise may cause further damage. When in doubt or when faced with challenging issues, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic or automotive service professional.
Power Steering Maintenance and Prevention
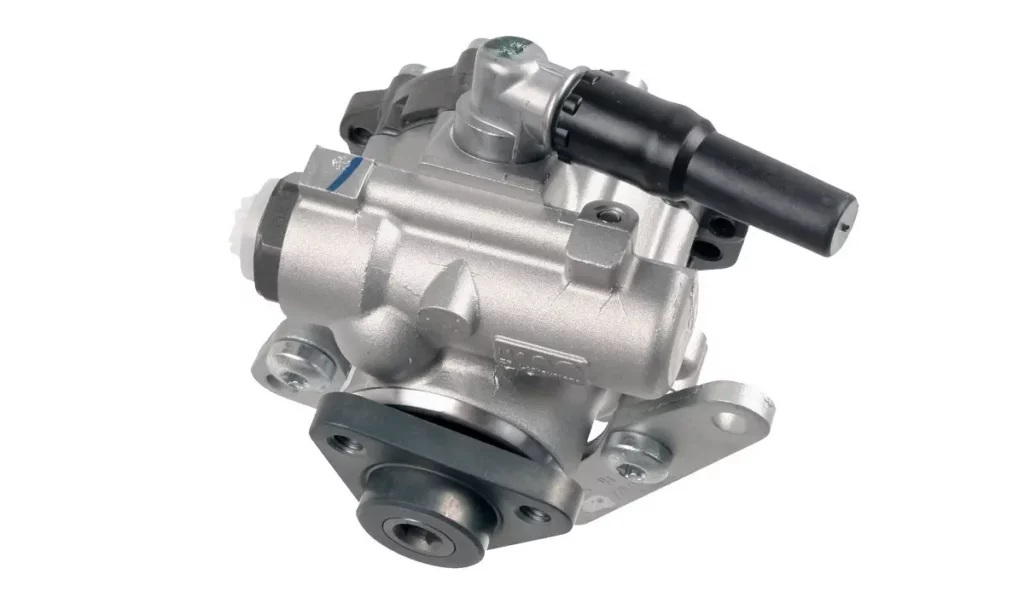

Regular maintenance and preventive measures are crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle’s power steering system. Here are some essential maintenance practices to keep in mind:
Check Power Steering Fluid Regularly – Inspect the power steering fluid level regularly and top it up if necessary. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended fluid type and specifications. If you notice a significant drop in fluid level or recurring low fluid levels, have the system inspected for potential leaks.
Perform Power Steering Fluid Flush – Over time, power steering fluid can become contaminated with dirt, debris, and moisture, leading to diminished performance. It is recommended to perform a power steering fluid flush as per the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Flushing the system helps remove old, degraded fluid and ensures optimal lubrication and hydraulic pressure.

Inspect Power Steering Belts and Pulleys – Regularly check the condition and tension of the power steering belts. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. Replace worn-out belts and ensure proper alignment and tension. Inspect the pulleys for any damage or misalignment that may affect belt performance.
Address Leaks Promptly – If you notice any power steering fluid leaks or dampness around hoses, seals, or connections, address them promptly. Leaks can lead to fluid loss, reduced hydraulic pressure, and potential damage to other components. Repair or replace the affected parts to prevent further issues.
Follow Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule – Adhere to the recommended maintenance schedule provided by the vehicle manufacturer. This includes regular inspections, fluid changes, and component replacements. Following the prescribed maintenance intervals helps identify and address potential problems before they escalate, ensuring the reliability of your power steering system.
Avoid Overloading the Steering System – Avoid putting excessive strain on the power steering system by avoiding sharp turns at high speeds or excessive force on the steering wheel. These actions can cause unnecessary stress on the system and lead to premature wear or failure.
By following these maintenance practices and taking preventive measures, you can extend the lifespan of your power steering system and minimize the risk of failures or costly repairs.
In conclusion, understanding the functioning of power steering systems, recognizing failure causes and symptoms, troubleshooting effectively, and implementing regular maintenance practices are essential for keeping your vehicle’s power steering system in optimal working condition.
Get Quality Power Steering Components at Bimmers.com!
In conclusion, power steering plays a critical role in modern vehicles, providing drivers with enhanced control and ease of maneuverability. Whether it’s a hydraulic power steering system or an electric power steering system, understanding how they work and recognizing potential failure causes and symptoms is vital for maintaining a safe and comfortable driving experience. Here at Bimmers.com, we offer a wide range of power steering components for all kinds of BMW models. Head over to our store, select your vehicle from the drop down menu, and find parts that are a guaranteed fit!