Your BMW is a precision-engineered marvel, combining luxury, performance, and cutting-edge technology. However, even the most sophisticated machines can encounter issues, and when it comes to engine performance, misfires can be a troublesome concern. Among the array of fault codes that can illuminate your BMW’s dashboard, the dreaded “29CD” stands out — the telltale sign of a Cylinder 1 misfire.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the 29CD BMW fault code, focusing on its association with Cylinder 1 misfire. Understanding the significance of this issue and quickly addressing it is vital to maintain your BMW’s exceptional performance and ensure its longevity.
As we explore the world of Cylinder 1 misfires, we’ll take a closer look at the diagnostic process involved, common causes behind this problem in BMW vehicles, and practical troubleshooting steps you can take to remedy the issue.
Understanding 29CD Cylinder 1 Misfire
When your BMW’s engine runs smoothly, it’s a symphony of mechanical harmony. However, a misfire disrupts this harmonious performance, leading to a host of problems. In essence, a misfire occurs when the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber fails to ignite as intended, causing a loss of power and efficiency.
What is a Misfire?
A misfire refers to the incomplete combustion of the air-fuel mixture in one or more cylinders of the engine. When the spark plug fails to ignite the mixture, the engine experiences a momentary hiccup in its power delivery, often felt as a rough idle, a noticeable vibration, or a significant drop in acceleration. While occasional misfires may not cause immediate damage, prolonged or frequent misfires can harm the engine and its components, leading to more severe issues over time.
How Fault Codes are Detected
Modern BMW vehicles are equipped with sophisticated onboard diagnostics (OBD) systems that continuously monitor the engine’s performance. When a misfire is detected in Cylinder 1, the DME logs the fault code “29CD” and illuminates the check engine light on your dashboard. This warning is a crucial indicator that something requires attention within the engine.
Reasons Behind Cylinder 1 Misfire
Numerous factors can contribute to a misfire in Cylinder 1 of your BMW’s engine. Some common causes include:
Ignition System Problems:
- Worn or fouled spark plugs
- Defective ignition coils
- Issues with the ignition control module
Fuel System Issues:
- Clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors
- Inadequate fuel pressure due to a failing fuel pump
- Fuel delivery problems
- Contaminated fuel
Mechanical Faults:
- Low compression in Cylinder 1
- Valve train issues
- Intake or exhaust manifold leaks
- Carbon deposits on valves or pistons
Impact of Cylinder 1 Misfire
Ignoring a Cylinder 1 misfire can have adverse consequences for your BMW. Not only does it result in reduced engine power and diminished fuel efficiency, but it can also lead to other problems. An unburnt air-fuel mixture can damage the catalytic converter over time, leading to costly repairs. Moreover, prolonged misfires can stress engine components, potentially resulting in severe engine damage if left unaddressed.
Diagnostic Procedures
When the check engine light illuminates in your BMW, it’s essential to retrieve the fault code associated with the Cylinder 1 misfire. You can do this using an OBD-II scanner, which connects to your car’s onboard diagnostic system. Once connected, the scanner will read and display the specific fault code “29CD,” confirming the presence of a Cylinder 1 misfire.
Basic Inspections
Before delving deeper into the diagnosis, perform some basic inspections to rule out simple issues that may trigger a misfire:
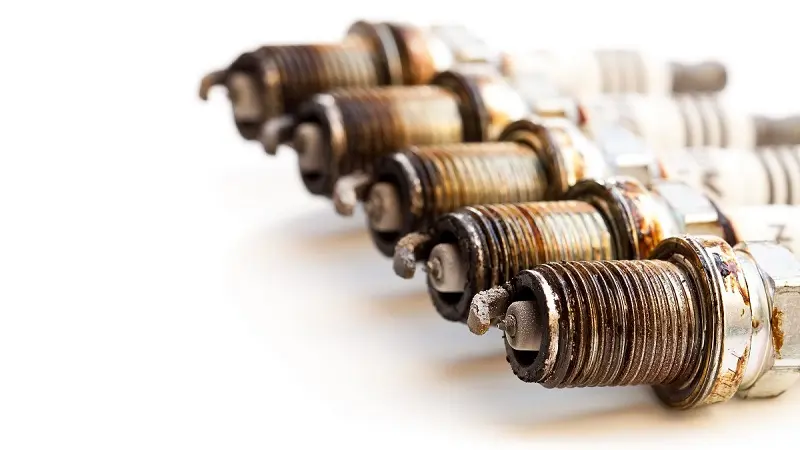
- Check Spark Plugs — Inspect the spark plugs for signs of wear, fouling, or damage. Worn-out spark plugs are a common cause of misfires and should be replaced if necessary.
- Inspect Ignition Coils — Examine the ignition coils connected to Cylinder 1 for any visible signs of damage or corrosion. Faulty coils can disrupt the ignition process, leading to misfires.
- Review Wiring and Connections — Ensure that all ignition system wiring and connections, including spark plug wires and harnesses, are secure and free from damage.
OBD Data Analysis
Using the OBD-II scanner, review live data from your BMW’s engine while the vehicle is running. Pay close attention to parameters related to Cylinder 1, such as fuel trim levels, misfire counts, and oxygen sensor readings. This data can offer valuable insights into potential issues causing the misfire.
Cylinder Compression Test
A cylinder compression test is a crucial step in diagnosing a Cylinder 1 misfire. This test determines the compression pressure within the cylinder, helping identify issues related to piston rings, valves, or head gasket leaks. Low compression in Cylinder 1 can point to mechanical problems that require attention.
Fuel System Inspection
A comprehensive inspection of the fuel system is vital to rule out fuel-related issues. This includes checking fuel injectors, fuel pressure, and fuel delivery. Clogged or malfunctioning injectors, low fuel pressure, or contaminated fuel can all lead to misfires.
Vacuum Leak Detection
Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and lead to misfires. Utilize a smoke machine or other suitable methods to identify and locate any vacuum leaks in the intake system.
By following these diagnostic procedures, you’ll be one step closer to uncovering the root cause of the Cylinder 1 misfire in your BMW. In the next section, we’ll explore the common causes behind this problem, providing you with valuable insights to address the issue effectively.
Common Causes of Cylinder 1 Misfire in BMWs
A Cylinder 1 misfire in your BMW can stem from various underlying issues. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for implementing the right solution and restoring your engine’s performance. Below are some common reasons behind Cylinder 1 misfires:
Ignition System Problems
- Worn or Fouled Spark Plugs — Over time, spark plugs wear out and develop carbon deposits, hindering their ability to produce a strong spark. This can lead to misfires in Cylinder 1. Regularly inspect and replace spark plugs according to BMW’s recommended intervals.
- Defective Ignition Coils — Faulty ignition coils can cause intermittent or consistent misfires. Each cylinder has its own ignition coil, and a malfunctioning coil may fail to deliver the necessary spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in Cylinder 1.
- Damaged Spark Plug Wires or Ignition Cables — If the spark plug wires or ignition cables connecting the ignition coils to the spark plugs are damaged or worn out, it can result in weak or no spark, leading to Cylinder 1 misfire.
Fuel System Issues
- Clogged or Malfunctioning Fuel Injectors — Fuel injectors can become clogged with debris or fail to open and close properly, affecting the fuel delivery to Cylinder 1. Insufficient fuel flow can cause a misfire.
- Inadequate Fuel Pressure — Low fuel pressure can lead to poor fuel atomization, affecting the air-fuel mixture’s combustion. It’s essential to ensure that your BMW’s fuel system maintains the correct pressure levels.
- Contaminated Fuel — Using low-quality or contaminated fuel can impact the combustion process, causing misfires. Ensure you fill up with high-quality fuel from reputable gas stations.
Mechanical Faults
- Low Compression in Cylinder 1 — Insufficient compression in Cylinder 1 can occur due to worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket. Low compression leads to incomplete combustion and misfires.
- Valve Train Issues — Problems with the valve train, such as a sticking valve or worn camshaft lobe, can disrupt the airflow and fuel mixture, resulting in misfires.
- Intake or Exhaust Manifold Leaks — Air leaks in the intake or exhaust manifold can introduce additional air into Cylinder 1, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture and misfires.
- Carbon Deposits — Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate on the intake valves and pistons. These deposits can disrupt the proper air-fuel mixture, contributing to Cylinder 1 misfire.
It’s important to note that while the above causes are common, a Cylinder 1 misfire can result from a combination of factors. To effectively resolve the issue, a systematic approach to diagnosis is necessary.
Troubleshooting and Fixing the Issue

Addressing a Cylinder 1 misfire in your BMW requires a methodical approach to pinpoint and resolve the root cause. Follow these practical troubleshooting steps to tackle the issue effectively:
Step 1: Address Ignition System Issues
If your spark plugs show signs of wear or fouling, replace them with high-quality, compatible ones recommended by BMW. Ensure the spark plug gaps are set correctly.
Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the ignition coils connected to Cylinder 1. If any coil shows abnormal resistance readings or is not functioning correctly, replace the faulty coil.
Step 2: Fuel System Inspection and Cleaning
If the fuel injectors are clogged or malfunctioning, consider cleaning them using a suitable fuel injector cleaner. In severe cases, it may be necessary to replace the faulty injectors.
Check the fuel pressure using a fuel pressure gauge to ensure it falls within the manufacturer’s specified range. If the pressure is low, investigate and repair any issues with the fuel delivery system.
Using a fuel system cleaner designed for BMW vehicles can help remove carbon deposits and improve fuel system performance.
Step 3: Conduct a Compression Test
Perform a cylinder compression test to assess the compression levels in Cylinder 1. If the compression is significantly lower than in other cylinders, it indicates potential mechanical problems that need to be addressed, such as worn piston rings or valve issues.
Step 4: Check for Vacuum Leaks
Inspect the intake manifold, intake hoses, vacuum lines, and hoses for leaks. Address any leaks found and ensure the intake system is airtight.
Step 5: Decarbonize the Engine
If carbon deposits are suspected to be the cause of the misfire, consider using a professional engine decarbonization service or perform a manual carbon cleaning procedure.
Step 6: Retest and Monitor
After performing the necessary repairs and maintenance, clear the fault codes using the OBD-II scanner and take your BMW for a test drive. Monitor the engine’s performance to ensure the misfire is resolved. If the misfire persists, reevaluate the diagnostic steps or consider seeking professional assistance.
Preventative Measures
Preventing Cylinder 1 misfires in your BMW involves a combination of regular maintenance, attentive driving, and proactive care. By following these preventative measures, you can minimize the risk of misfires and ensure your BMW’s engine operates smoothly:
Follow BMW’s Service Schedule
Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for your BMW. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections, helps keep your engine in top condition.
Replace Spark Plugs and Ignition Components
Replace spark plugs and ignition components at the recommended intervals or if signs of wear and tear are observed. Genuine, OEM or reputable aftermarket parts are essential for optimal performance.
Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors
Periodically clean fuel injectors to prevent clogging and ensure proper fuel delivery. If injectors are faulty, replace them quickly.
Use High-Quality Fuel
Opt for high-quality gasoline from reputable gas stations. Quality fuel helps maintain engine performance and reduces the risk of fuel system issues.
Check for Vacuum Leaks
Regularly inspect the intake manifold, vacuum lines, and hoses for any signs of leaks or damage. Address vacuum leaks quickly to maintain the integrity of the air-fuel mixture.
Regularly Monitor Engine Performance
Stay attentive to any changes in your BMW’s engine performance, such as rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, or hesitation during acceleration. Quickly address any unusual behavior to prevent potential issues from escalating.
By incorporating these preventative measures into your routine, you can ensure that your BMW’s engine remains in excellent condition and minimize the risk of Cylinder 1 misfires. Remember that proactive care and attention to your vehicle’s needs are vital for maximizing its performance and longevity.
Fix the 29CD BMW Code with Bimmers.com!
A 29CD BMW code indicating a Cylinder 1 misfire can be an unsettling experience for any BMW owner. However, armed with knowledge of the common causes and equipped with proper diagnostic procedures, you can address the issue effectively. Regular maintenance, attentive driving, and proactive care are essential to prevent Cylinder 1 misfires and maintain your BMW’s exceptional performance.
If you’re searching for high quality parts to solve your misfiring BMW, you’re in the right place! Here at Bimmers.com, we offer a wide range of premium parts that will keep your BMW running smoothly. Check out our catalog and find BMW parts that are a guaranteed fit for your car!